Understanding Cell Lymphoma and Its Impact on Patients
Cell Lymphoma is a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic system, which is a crucial part of the immune system. This cancer affects a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, which play a significant role in defending the body against infections and diseases. The diagnosis of cell lymphoma can be overwhelming, and it is essential to understand the disease and its impact on patients to identify the best possible treatment options.
In recent years, immunotherapy has emerged as a promising treatment for cell lymphoma. Immunotherapy harnesses the power of the immune system to fight cancer cells, offering a more targeted and less toxic approach compared to traditional treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation. In this article, we will delve into the role of immunotherapy in treating cell lymphoma and how it can improve the prognosis for patients.
Unlocking the Potential of the Immune System
Our immune system is designed to protect us from harmful invaders such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. However, cancer cells are often able to evade the immune system by disguising themselves as healthy cells or by creating an immunosuppressive environment. Immunotherapy aims to boost the immune system's ability to recognize and attack these cancer cells, allowing for a more effective and targeted treatment.
There are several types of immunotherapy used in treating cell lymphoma. Some of these treatments work by stimulating the immune system to attack cancer cells, while others involve the use of laboratory-made immune system proteins that can directly target cancer cells. The choice of immunotherapy depends on the individual patient's condition and the specific type of lymphoma.
Monoclonal Antibodies: A Targeted Approach
One of the most common types of immunotherapy used for cell lymphoma is monoclonal antibodies. These are laboratory-made proteins that mimic the immune system's ability to recognize and attack specific targets on cancer cells. Monoclonal antibodies can be designed to bind to specific proteins or other molecules on the surface of cancer cells, helping the immune system to identify and attack these cells more effectively.
In cell lymphoma, one of the most widely used monoclonal antibodies is Rituximab, which targets the CD20 protein found on the surface of many lymphoma cells. By binding to this protein, Rituximab helps the immune system to recognize and destroy the cancerous cells, leading to improved treatment outcomes for many patients.
Checkpoint Inhibitors: Overcoming Cancer's Defenses
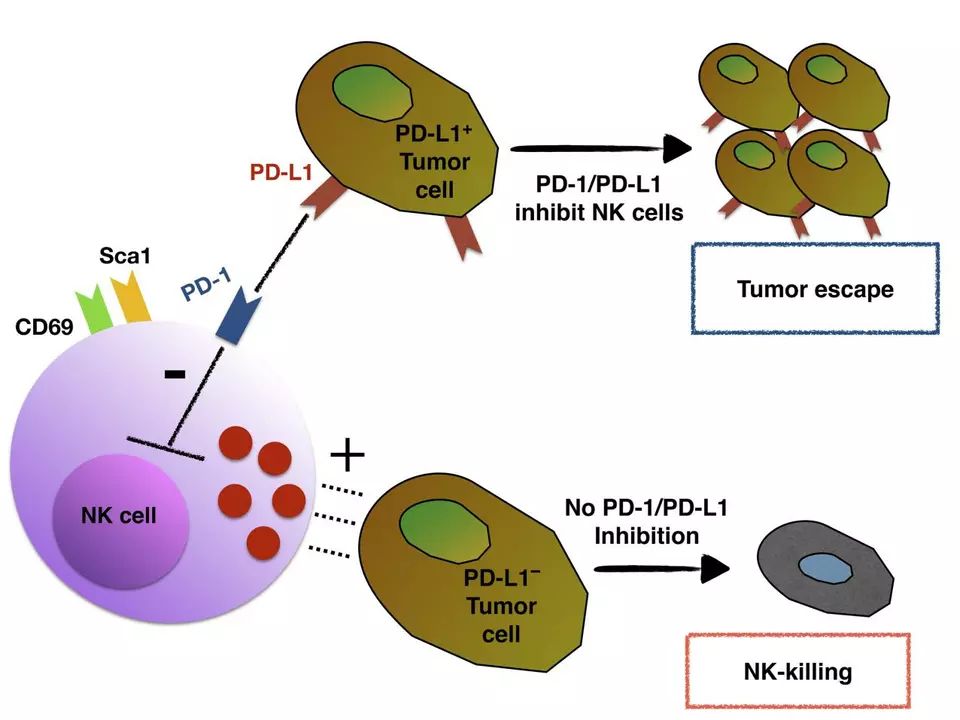
Another type of immunotherapy used in treating cell lymphoma is checkpoint inhibitors. These drugs work by blocking specific proteins on the surface of cancer cells, which are responsible for preventing the immune system from attacking them. By inhibiting these checkpoints, the immune system can more effectively target and eliminate the cancer cells.
Some checkpoint inhibitors currently used in the treatment of cell lymphoma include pembrolizumab and nivolumab, which target the PD-1 protein. These drugs have shown promising results in clinical trials, particularly for patients with relapsed or refractory lymphomas.
Adoptive T-Cell Therapy: A Personalized Treatment
Adoptive T-cell therapy is a form of immunotherapy that involves collecting a patient's own immune cells, modifying them in the laboratory to enhance their cancer-fighting capabilities, and then reintroducing them back into the patient's body. This personalized treatment has shown great promise in treating certain types of cell lymphoma, particularly those resistant to traditional therapies.
One example of adoptive T-cell therapy is CAR-T cell therapy, which involves engineering a patient's T-cells to recognize and attack specific targets on the surface of cancer cells. This treatment has demonstrated remarkable success in treating aggressive forms of lymphoma, leading to durable remissions in some patients who had exhausted all other treatment options.
Immunomodulatory Drugs: Boosting the Immune Response
Immunomodulatory drugs are another form of immunotherapy used in treating cell lymphoma. These drugs work by stimulating the immune system to mount a more effective response against cancer cells. Some commonly used immunomodulatory drugs include lenalidomide and thalidomide, which have shown to be effective in treating certain types of lymphoma.
These drugs are typically used in combination with other treatments such as chemotherapy or monoclonal antibodies, offering a multi-pronged approach to fighting the disease.
Combining Immunotherapy with Traditional Treatments
While immunotherapy has shown great promise in treating cell lymphoma, it is often used in combination with traditional treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy. This combined approach can help to enhance the overall effectiveness of the treatment, leading to better outcomes for patients.
For example, the combination of Rituximab with chemotherapy has become a standard treatment for many types of cell lymphoma, improving the chances of remission and survival for many patients. Further research is ongoing to determine the optimal combinations of immunotherapy and traditional treatments for different types of lymphoma.
Managing Side Effects of Immunotherapy
While immunotherapy offers a more targeted approach to treating cell lymphoma, it is not without its side effects. Some patients may experience immune-related side effects, such as inflammation, rash, or fever, as a result of their immune system's heightened activity. Other side effects may be specific to the type of immunotherapy being used, such as infusion reactions or cytokine release syndrome.
It is crucial for patients to communicate any side effects they are experiencing to their healthcare team, as prompt intervention can help to minimize discomfort and prevent serious complications. In some cases, the side effects may necessitate a change in the immunotherapy regimen or the use of additional medications to manage symptoms.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Immunotherapy in Treating Cell Lymphoma
Immunotherapy has already made a significant impact on the treatment of cell lymphoma, offering new hope to patients who may not have responded well to traditional therapies. As research continues to advance, we can expect to see more innovative immunotherapy approaches being developed and tested in clinical trials.
By staying informed about the latest developments in immunotherapy and collaborating closely with their healthcare team, patients with cell lymphoma can make informed decisions about their treatment options, ultimately leading to improved outcomes and a better quality of life.
Aman Vaid
June 2, 2023 AT 02:16Immunotherapy has fundamentally altered the therapeutic landscape for cell lymphoma over the past decade.
By harnessing the capacity of cytotoxic T‑cells, monoclonal antibodies, and checkpoint blockade, clinicians can now target malignant clones with unprecedented specificity.
Rituximab, the anti‑CD20 monoclonal antibody, remains the cornerstone of first‑line regimens, reducing relapse rates in both indolent and aggressive subtypes.
Nevertheless, resistance mechanisms such as CD20 antigen loss or downstream signaling alterations necessitate alternative strategies.
Checkpoint inhibitors, particularly anti‑PD‑1 agents like pembrolizumab, have demonstrated activity in relapsed‑refractory cases, albeit with heterogeneous response rates.
The heterogeneity of tumor microenvironments dictates that a single modality rarely achieves durable remission in isolation.
Consequently, combination approaches-pairing CAR‑T cell therapy with a short course of chemotherapy-are being evaluated in several phase II trials.
Early data suggest that bridging chemotherapy can reduce tumor burden, thereby mitigating cytokine release syndrome during subsequent CAR‑T infusion.
Moreover, immunomodulatory drugs such as lenalidomide can potentiate the effector function of T‑cells by downregulating regulatory cytokines.
In practice, the decision matrix incorporates patient age, comorbidities, and prior exposure to cytotoxic agents.
For elderly patients with limited performance status, a rituximab‑plus‑lenalidomide regimen may provide a tolerable yet efficacious alternative.
Conversely, younger patients with high‑grade disease often benefit from an upfront autologous stem‑cell transplant following CAR‑T consolidation.
It is equally important to monitor immune‑related adverse events, as early intervention with corticosteroids can prevent progression to severe organ dysfunction.
Multidisciplinary coordination among hematologists, immunologists, and supportive care teams ensures that toxicities are managed proactively.
Ultimately, the continued integration of translational research with clinical trial accrual will define the next generation of immunotherapeutic protocols for cell lymphoma.
xie teresa
June 2, 2023 AT 02:50I completely understand how overwhelming the treatment journey can feel, and I'm hopeful that these advances bring real relief.
Srinivasa Kadiyala
June 2, 2023 AT 03:23While the enthusiasm surrounding immunotherapy is commendable, it is essential to recognise that the evidence base is not uniformly robust; many studies rely on small cohorts, short follow‑up periods, and surrogate endpoints, which limit the generalisability of the findings.
Moreover, the high financial burden associated with CAR‑T products, checkpoint inhibitors, and novel monoclonal antibodies raises concerns about accessibility, especially in low‑resource settings; cost‑effectiveness analyses are still in their infancy, and without clear health‑economic data, widespread adoption remains questionable.
In addition, the risk of severe immune‑related toxicities, such as cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity, cannot be dismissed as merely manageable side effects; despite prophylactic measures, a subset of patients experience life‑threatening complications that may outweigh potential benefits.
Therefore, a balanced appraisal must weigh not only the promising response rates but also the heterogeneity of outcomes across diverse patient populations, and the realistic feasibility of integrating these modalities into standard care pathways.
Alex LaMere
June 2, 2023 AT 03:56The data you cite are from early‑phase trials; real‑world outcomes differ. 😬
Dominic Ferraro
June 2, 2023 AT 04:30Stay hopeful the science keeps moving forward and patients are seeing new options emerge. Together we can look to brighter days ahead.